A few years ago, an intern called me and insisted that the blood bank staff was being uncooperative. This young physician stated that his attending physician had asked him to order a “Direct and Indirect Coombs,” and he had done so. The blood bank technologist told him that both tests had been done, but this fine young doctor couldn’t understand why there wasn’t a result in the computer labeled as “Indirect Coombs.” He said that he could accept the result called a “direct antiglobulin test,” but the technologist would not issue a report that was labeled “Indirect Coombs” (he mentioned that his attending was very demanding, and I am pretty sure that he was afraid for his life, but I may have misinterpreted the panic in his voice and the fact that I could hear his heart pounding through the phone). He somewhat forcefully “requested” that I tell my staff to issue an appropriate report.
If you’re thinking at this point that conflict resolution training should be part of medical school curriculum, you are not alone. And, if you see nothing wrong with what this young doctor demanded, chances are you don’t understand the Direct and Indirect Antiglobulin tests (DAT and IAT, respectively) quite as well as you could!
You aren’t alone, though; these are two of the most mysterious laboratory tests to clinical staff, students, and less experienced laboratorians. This post will describe the differences and similarities between the DAT and the IAT, and how each of them is used. Tuck this away as, regardless of your role in patient care, this is a question you’re likely going to need the answer to at some point.

What’s in a name?
Let’s just start with the “name thing!” In my experience, most clinicians call these tests “Indirect Coombs” and “Direct Coombs,” while most blood bankers refer to them by their more proper names: “Indirect Antiglobulin Test” (IAT) and “Direct Antiglobulin Test” (DAT). That difference is where much of the confusion for clinicians arises, because while everyone is talking about the same tests, they are speaking in different dialects!
Beyond dialects, though, there is a slightly longer explanation for the miscommunication frequently invoked by these two tests, and it starts with a look at the two types of immunoglobulin (antibodies) we worry about most in the blood bank: IgG and IgM. These two antibody types react in different ways with target antigens on red blood cells (RBCs).
IgG vs. IgM
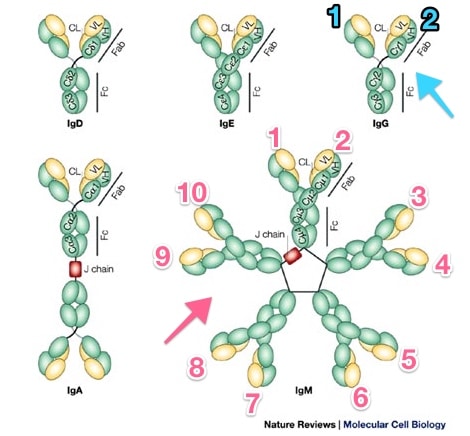
Immunoglobulins; Note IgG vs. IgM
Rojas R et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002

Robin Coombs
Let’s start at the end
The principle of the antiglobulin test – direct or indirect – is this: An antibody targeted against human proteins will bind to those proteins already attached to RBCs and cause visible agglutination. That sentence is the key to unlocking the mystery of both the DAT and IAT. Let’s break it down part by part.
First: “An antibody targeted against human proteins…”
Anti-human globulin is prepared by injecting a non-human (traditionally rabbits and more recently mice) with human antibodies and/or complement. When the animals produce their own antibodies against the human proteins, the antibodies can be harvested directly from the animal’s serum (these are “polyclonal” antibodies, containing a mix of specificities). Alternatively, the plasma cells making the antibodies can be isolated and fused with eternally dividing malignant plasma cells, and the resulting antibodies are purified to make “monoclonal” antibodies (by definition, reacting against only one epitope). Whether monoclonal or polyclonal, anti-human globulin simply seeks out human immunoglobulin and/or human complement proteins.
Second: “…will bind to those proteins already attached to RBCs…”
If a target antibody or complement component is already attached to an RBC that is being tested (either because we mixed an RBC with an antibody in a test tube in the laboratory or the antibody or complement attached itself to the RBC in the body), AHG is made to be very good at binding directly to that target antibody and/or complement.
Third: “…and cause visible agglutination.”
Visible agglutination occurs when the antiglobulin reagent binds to either antibody or complement on the RBC and “bridges” adjacent cells into a clump (see images below). What you see is the LAST step of ANY antiglobulin test, either the “direct” or “indirect” version. The difference between the DAT and the IAT comes from HOW and WHERE the RBCs being tested get coated with antibody.
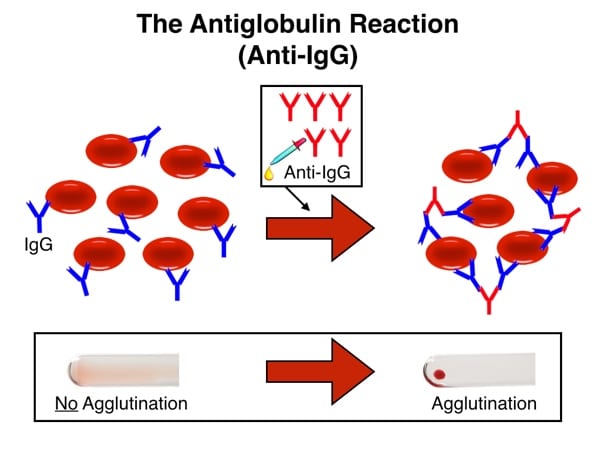
Reaction with IgG-coated RBCs and anti-IgG
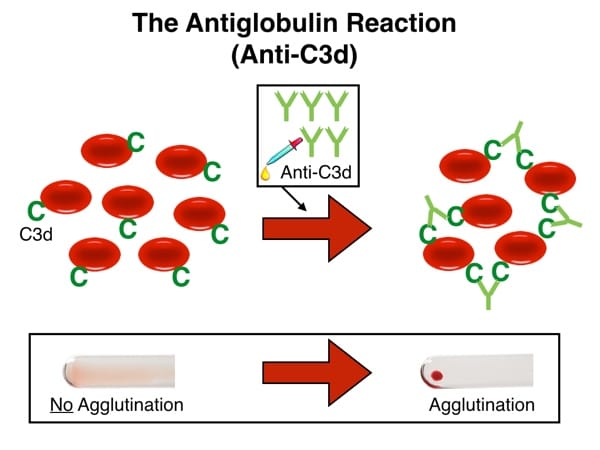
Reaction with C3d-coated RBCs and anti-C3d
Now, let’s go back to the beginning
So, now that you understand the last step of any antiglobulin test, whether IAT or DAT, let’s go back and describe how we start these tests, and that will help you understand why one is called “direct” and one “indirect.” It really all comes down to how the antibody or complement gets attached to the RBCs in the first place!
The IAT; Tricky, tricky blood bankers!
The Indirect Antiglobulin Test is incredibly common, but most people don’t realize that fact. Nearly every time blood banks prepare a person for transfusion, for example, we do an IAT. To be tricky, though, we usually don’t CALL it an IAT!
Pretransfusion testing for a potential RBC transfusion recipient includes at least three items:
- ABO grouping
- Rh grouping
- Test for “unexpected” (non-ABO) antibodies
The last test is commonly known as an “antibody screen,” and it can be performed in several different ways and on multiple different testing platforms (a topic for another post). Regardless of how we do it, an antibody screen must, by definition, include an evaluation using anti-human globulin. In other words, all antibody screens are indirect antiglobulin tests.
To perform the IAT, the patient’s serum or plasma is mixed with RBCs from a group O blood donor with a known RBC antigen profile and incubated. Then, the cells are washed to remove any unbound antibodies, followed by addition of the AHG reagent. In other words, the antibody-RBC interaction that causes a positive IAT occurs in the laboratory, and thus an indirect interaction between antibodies/complement and RBCs. Here’s how it looks:
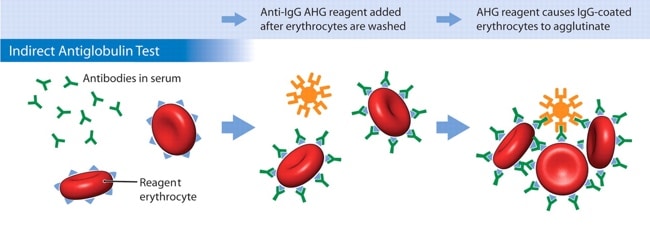
Image courtesy Dr. Mark Yazer; Can Med Assoc J 31 Jan 2006
So, when a clinician or nurse asks about an “Indirect Coombs,” what they mean, whether they know it or not, is, “has an antibody screen been done?” That fact gets really lost on clinicians sometimes, and it’s understandably confusing. Think of it like this: An antibody screen is a laboratory test name which utilizes an Indirect Coombs, or IAT, test method. One is a test, one is a test method. It’s the same as saying, do you want chicken for dinner, or fried chicken? One is a food, one is a food preparation technique. See the difference?
Note: The antibody screen is not the only situation when an IAT is done, just the most common. See the list at the bottom of the post for the most common uses of the IAT.
The DAT; Less common but simple
The Direct Antiglobulin Test, on the other hand, is much less complex. In a DAT, the RBCs are simply removed from the patient’s body, washed, and immediately mixed with the AHG reagent. In other words, the DAT is designed to detect the presence of something coating the RBC in the body, not in the laboratory. It is “direct” because we don’t do anything to make the coating antibodies and the RBCs interact; we are simply evaluating whether or not such an interaction already occurred in the body. Here’s a DAT, for comparison:
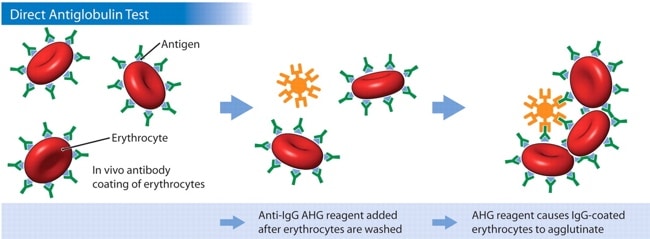
Image courtesy Dr. Mark Yazer; Can Med Assoc J 31 Jan 2006
Again, notice that the last step is exactly the same in the DAT and the IAT! The only difference is in the first part: Where the antibody-complement-RBC interaction happens (In the body: DAT. In the lab: IAT).
Remember that while the images above show antibodies against IgG, the anti-human globulin reagents I described above may also target complement components on the RBC. When antibodies bind to RBCs (especially IgM antibodies, but also IgG to a lesser extent), complement proteins may also be bound. We can use AHG that reacts against either complement components (we typically call this “anti-C3”) or IgG (“anti-IgG”) or BOTH (“polyspecific” AHG). Most facilities use a polyspecific AHG reagent first when performing a DAT. If that reaction is positive, they will do separate testing using anti-C3 and anti-IgG to tease out more precisely what caused the polyspecific DAT test to be positive.
OK, I hope that helps you understand the differences between the two tests. Let’s close this post by listing the most common situations where the IAT and DAT are used.
Direct Antiglobulin Test (aka, “Direct Coombs,” “DAT”):
- Transfusion reaction workup (demonstrates that incompatible RBCs have been transfused)
- Hemolytic anemia workup (demonstrates if the hemolysis is due to antibodies or complement coating the RBCs)
- Cord blood samples when evaluating for incompatible maternal antibodies (added 4/27/16)
Indirect Antiglobulin Test (aka, “Indirect Coombs,” “IAT”):
- Pre-transfusion recipient antibody detection testing (antibody screen; detects non-ABO antibodies)
- Major crossmatch, with history of or presently identified significant antibodies
- In Rh typing, when an initial test for D is negative (“weak D test”)
- In laboratory settings, for testing RBCs for the presence of certain antigens
I discussed the interpretation of the DAT with the brilliant Sue Johnson on the Blood Bank Guy Essentials Podcast in February 2017. Check it out!
By the way, I explained to the young doctor I mentioned at the top that the “indirect Coombs” test that he was looking for was, in fact, just the antibody screen. At that point, he grumbled something that sounded like “well, why don’t they just CALL it that?” and we parted ways. Just another happy day in the life of a hospital blood banker!










Brilliant – as ever!
Thank you, Malcolm!
I think you need a shiny cape. This article just elevated you to superhero status in my book.
Not even close, Sue, but thanks!
Crystal clear. Thank you.
If a BB topic is not clear to me, I go to bbguy website. Thank you for all you do. I used this website a lot when I was preparing for my SBB exam. Very helpful. Thanks.
I’ve saved the home page in preparation for the SBB program! It’s nice to know it’ll be helpful!
Hi Joe
Both informative and humorous as always! One small “correction”, I was lucky enough to attend a lecture by Robin coombs in Bristol (UK) in the 1980’s when he happily referred to “my test”, so I don’t think he minded the name too much!
Julie, thanks for that comment! I had always heard that he didn’t like it being called by his name (and I also read somewhere that another group had published the same basic idea several decades earlier but possibly in another language, unbeknownst to the Coombs group), but I’m glad that he took pride in it! It is one of the most spectacular contributions to transfusion safety we’ve ever seen! I just wish it didn’t confuse people so much.
Just wow! Thank you. You are the go to man for blood bank information
AHG used in the last step belongs to igM or igG???
Generally speaking, it is a high-titer and highly active IgG, though there are exceptions. Monoclonal anti-C3d is commonly IgM, for example. Thanks for the question!
LOL – Tyrannosaurus Rx and Doctor Octopus. My BB world will never be the same!!!! Fantastic article 🙂
Glad you liked it, Sandra! My specialty: Using weird stuff to help people remember things!
I will forever think of IgG as T rex and IgM as Doctor Octopus now!
This is brilliant! I always understood the difference between IgG and IgM antibodies but I never could grasp the real difference between the two tests. The comparison of the DAT and IAT to ‘in the body’ versus ‘in the lab’ really got it straight in my head. Informative and funny blog post as always. Thanks Joe!
Carly, I’m so glad that the post was helpful to you! I am trying to finish a post on the meaning of a positive DAT this week, so stay tuned! Thanks for writing.
Joe
Finally someone showed me the distinctions between the two tests in a way that is easy to understand! A couple of my classmates and myself accidentally stumbled upon your podcasts and honestly, if it hadn’t been for you, we would utterly fail our Blood Bank course! Love your methods and your humor!
Gail, I’m glad you found it useful! I’m also honored to be of service to you and your classmates. As for my humor, well, I’m an unashamed goofball, so I’m just glad not to annoy you!
Joe
Great review material before my exam! Thank you Dr. Joe Chaffin, as always!!!
I’m honored to help you!
-Joe
I myself tried to donate blood but tested positive for these antibodies….. could I get a transfusion if I needed it?….curious
Roxanne, if you mean that you were told you have a positive DAT and that kept you from donating, then in most cases, you would still be able to get a transfusion if you needed to. Please consult with a local transfusion medicine expert for more information, as that expert could more fully evaluate your situation.
-Joe
If one has a positive indirect Coombs test will they also be positive for a direct test?
Regena, the answer to this is “not necessarily!” The IAT (indirect antiglobulin test) detects the presence of an antibody that will coat RBCs in the laboratory, or in a test tube, gel column, or whatever. The DAT (direct antiglobulin test) only detects whether or not the person being tested has either antibodies or complement on their RBCs in the body. The post above discusses this critical difference. So, for example, if someone who is D-negative develops anti-D, they will have a positive IAT (we would just call that an antibody screen), but not a positive DAT (unless it was positive for some other, unrelated reason). However, what I wrote isn’t always true. Imagine another case where someone has an autoantibody that reacts against all cells, including her own. In that case, both the IAT and the DAT would be positive because of that antibody. I hope that helps!
-Joe
why don’t they write med school books in this style? I’ve been trying to understand this topic from the “Hoffbrand essential hematology” and from THE Harrison but your blog really gets the work done. Thank you very much!
I’m very glad you found it useful, Chiara! I think that medical textbooks are hampered by too much formality, and that’s probably the way they have to be. For me, I can be as silly as I want, as long as I’m accurately portraying the information, so I have that advantage over medical text writers.
-Joe
You deserve a crown! Your content here help a lot with my discussion to my immunohematology students. I like the way you presented a technical topic to a no-brainer explanation.
Glad it was helpful, Terence!
-Joe
BB Guy,
I know not to centrifuge a specimen prior to performing the DAT, but what I can’t remember is WHY that is the case. Can you refresh my memory?
You are testing the red cells in a DAT. There is no need to separate the plasma from the cells prior to the DAT. You will be washing the cells.
Just starting my Job as a lead – biomedical scientist of a Hospital blood bank in Austria. Your blog is what i will suggest all my student-interns, young doctors,… .
Keep it up!
Sincerely
Mike
I’m honored you feel that way, Mike! Best of luck.
-Joe
As a current MLS student intern this blog reminds me of hearing blood bank techs talking about physicians on the phone demanding that FFP (kept frozen at this laboratory as we are not any level of trauma) be sent down to ER immediately. XD
I can’t describe it enough, but in simple word THANK YOU DR. I thank my instructor who introduced me to your videos!
You are welcome! Glad you are finding the information useful.
-Joe
I am trying to understand the answer to these questions if you could help? If you have a positive IAT and a negative DAT what antibody do you expect? And if you have a positive IAT and DAT what antibody is most likely the cause? From my reading it sounds like an autoantibody would be he cause if both positives, but I thought alloantibodies are the causes of hemolytic reactions from a transfusion for example which would be an alloantibody right?
Hi Emily, and thanks for writing. I’m always careful when I’m answering questions like this because it sounds like it may be part of an assignment, and I don’t like to wade in and spoil another teacher’s efforts. But, since it’s been over a week since you wrote this, I’ll just say a couple of things. First, the test you are referring to as an IAT certainly is an indirect antiglobulin test, but blood bankers never refer to it that way! We call it either an “antibody detection test” (more commonly, “antibody screen“), or if it involves a full investigation of an unknown antibody, it’s an “antibody identification panel.” So, if you said a “patient has a positive IAT,” I’d say, “oh, his antibody screen is positive?”
So, generally speaking, someone with a positive antibody screen and a negative DAT most commonly has an alloantibody, while someone with a positive antibody screen AND a positive DAT may have either an autoantibody, an autoantibody PLUS an alloantibody, OR an alloantibody reacting against recently transfused red blood cells from a donor. So, the answer is not simple.
You are correct that most hemolytic reactions are caused by alloantibodies in a a patient that react against substances on red blood cells they receive (but the most common ones are caused by antibodies to ABO antigens like anti-A and anti-B). Autoantibodies can also cause hemolysis, but just by attacking the patient’s own red blood cells. It’s more complex that that, but that should give you a start.
-Joe
Thank you so much Joe Chaffin. You really make my life easier in so many ways. You are the master
I’m very honored to be of help to you, Vidda.
-Joe
In the images, the yellow Anti-IgG AHG looks like IgM but with an extra “arm”. An Hexamer? Should AHG by IgG shaped? I am probably wrong. Thank you for your knowledge.
Fantastic. Been trying to learn this for years. Now I actually truly get it.
I’m very glad, Eric! Thanks for letting me know.
-Joe
Hi, Joe. I work in a small lab where we don’t do blood bank so I’ve forgotten everything I learned in school. This post helps A LOT. Thank you!
Hi, Joe! I’m now working in a hospital lab where blood bank is really busy and this once again helped me understand the theory behind the procedure manuals I’m learning! Thanks so much!
This is amazing ,, can’t be more clear.
Thank you
hi’ if we run out of coombs, how do we do a cross match.
thanks
I am about to take my ASCP in less than a month and I’m still a bit struggling with the difference of these two, and I have no words. This is the clearest explanation I found. Your glossary helps
I hope it went well, Dinne! Thanks for the kind words.
-Joe